Glossary
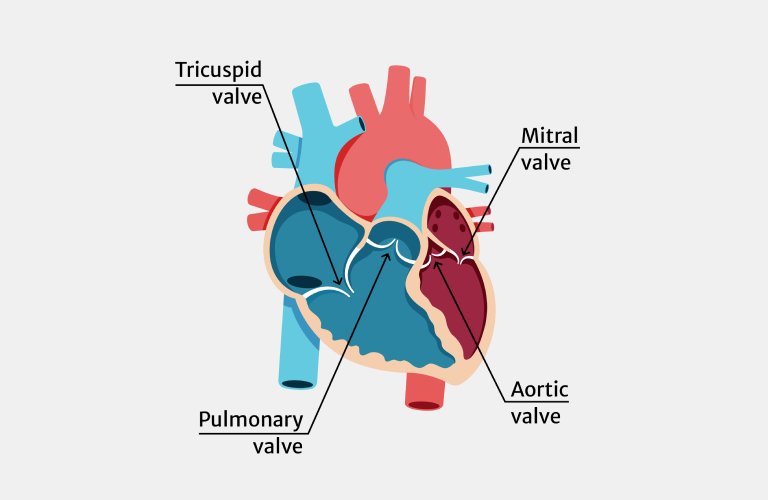
This glossary is available to help you understand complicated terms you will see on this website and may hear from your cardiologist, TAVR Doctor, or Heart Team as you learn about severe symptomatic aortic stenosis, also known as heart valve failure. Be sure to check with your doctor if you have any questions.







 Australia
Australia
 Brazil
Brazil
 Canada - French
Canada - French
 China - Taiwan
China - Taiwan
 Denmark
Denmark
 Finland
Finland
 Germany
Germany
 Italy
Italy
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Norway
Norway
 South Korea
South Korea
 Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
 Sweden
Sweden
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 United States
United States